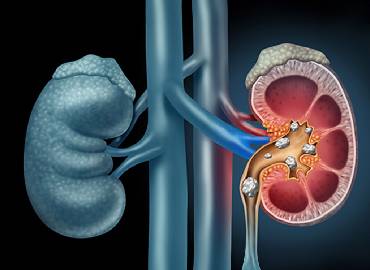
Kidney stones are hard mineral deposits that form in the kidneys and can obstruct the urinary tract.
Types:
- Calcium stones: The most common, often linked to high calcium or oxalate intake.
- Uric acid stones: Form in acidic urine, often related to gout or high-purine diets.
- Struvite stones: Often associated with urinary tract infections.
- Cystine stones: Rare, caused by a genetic disorder.
Treatment:
- Hydration: Drinking plenty of fluids helps prevent stone formation.
- Medications: Pain relief (NSAIDs), alpha-blockers to relax the ureter, or medications to dissolve uric acid stones.
- Surgical treatments: Lithotripsy (shockwave therapy), ureteroscopy, or percutaneous nephrolithotomy for larger stones.
Outcome: Stones often pass naturally with adequate hydration, but larger or more complex stones may require medical or surgical intervention.

